Introduction and The Advantages of Smart Homes
Introduction: The Dawn of Fully Smart Living
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, the concept of a “smart home” has shifted from a futuristic idea to a tangible lifestyle for millions. A fully smart home integrates Internet of Things (IoT) devices that connect, communicate, and automate various home functions—lighting, security, climate control, entertainment, and more—offering an unprecedented level of convenience and control.
But what exactly does living in a fully smart home mean? How does it transform daily routines, energy consumption, safety, and comfort? And perhaps most importantly, is it worth the investment and effort?
This first part of our in-depth series will explore the numerous advantages of fully smart homes, illustrated by real-world examples, expert opinions, and current industry data. By the end, you will understand why so many homeowners are embracing this lifestyle and how it can positively impact your life.
The Advantages of Fully Smart Homes
1. Unmatched Convenience and Automation
Imagine arriving home after a long day, and your house has already prepared itself: lights turn on softly, your preferred music playlist starts, the thermostat adjusts to the perfect temperature, and your smart oven begins preheating. This is the promise of automation powered by a fully smart home.
a. Voice and App Control
Thanks to virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri, controlling your entire home can be as simple as speaking a command or tapping a smartphone app. Whether you want to turn off the bedroom lights from the couch or lock the front door while driving away, these actions are at your fingertips.
b. Automated Routines
Smart home ecosystems allow you to program routines triggered by time, location, or events. For example:
-
Morning Routine: Curtains open, coffee machine starts, news briefing plays.
-
Away Mode: Lights turn off, security cameras activate, thermostat lowers.
-
Sleep Mode: Doors lock, lights dim, temperature adjusts for comfort.
According to a 2024 study by Statista, over 60% of smart home users reported that automation improved their daily routines’ ease and efficiency significantly.
2. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Energy management is among the most impactful benefits of smart homes. Automated devices adjust energy use based on presence, habits, and external conditions.
a. Smart Thermostats
Thermostats like the Google Nest and Ecobee learn your schedule and preferences, optimizing heating and cooling cycles to save energy without sacrificing comfort. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) notes that smart thermostats can reduce energy bills by up to 12%.
b. Smart Lighting
LED smart bulbs with motion sensors and daylight harvesting capabilities ensure lights are used only when necessary. Philips Hue, for instance, allows customizable scenes and schedules to avoid unnecessary usage.
c. Energy Monitoring
Advanced energy monitors track household energy consumption in real-time, providing insights into which appliances use the most power and suggesting ways to reduce waste. This data-driven approach enables better budgeting and environmental responsibility.

Introduction-The-Intersection-of-IoT-and-AI-Enhancing-Smart-Home-Experiences-DM-WebSoft-LLP
3. Enhanced Security and Safety
A fully smart home significantly upgrades your security posture with integrated, proactive solutions.
a. Video Doorbells and Surveillance Cameras
Devices like Ring and Arlo provide 24/7 live video feeds accessible remotely. Their AI-powered motion detection reduces false alerts by distinguishing between humans, animals, and objects.
b. Smart Locks and Access Control
Smart locks enable keyless entry with PIN codes or smartphone apps, allowing you to grant temporary access to guests or service providers. Many models also track who enters and when, enhancing security and accountability.
c. Environmental Sensors
Smoke detectors, carbon monoxide sensors, and water leak detectors integrated into your smart home system can alert you instantly and trigger automated responses like shutting off water valves or activating ventilation.
4. Personalized Comfort and Accessibility
Smart homes cater to individual preferences and needs, enhancing comfort and accessibility.
a. Customizable Environments
From adjustable lighting hues to zoned temperature control, smart devices let you personalize your environment room-by-room. For example, smart blinds can adjust based on sunlight intensity, maintaining optimal natural light and privacy.
b. Assistance for People with Disabilities
Voice control, automated door openers, and remote monitoring enable greater independence for people with mobility or sensory challenges, improving quality of life and safety.
5. Increased Home Value and Market Appeal
Modern homebuyers increasingly prioritize smart home features. According to the National Association of Realtors 2024 report, 72% of buyers view smart technology as a valuable asset that can increase property value and attract offers.
Case Study: The Thompson Family’s Smart Home Journey
The Thompsons, a family of four from Austin, Texas, converted their traditional home into a fully smart residence over 18 months. They installed smart thermostats, lighting, security cameras, locks, and an automated irrigation system.
-
Energy savings: They reduced their utility bills by 18% within the first year.
-
Convenience: Morning routines saved 30 minutes daily.
-
Security: Remote monitoring gave them peace of mind while traveling.

futurehomeshi_smart homes with IOT
Table 1: Comparison of Key Smart Home Devices for Convenience and Energy Savings
| Device Type | Popular Models | Average Cost | Key Benefit | Estimated Energy Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Thermostat | Google Nest, Ecobee | $120 – $250 | Optimizes heating/cooling | Up to 12% |
| Smart Lighting | Philips Hue, LIFX | $15 – $50/bulb | Automated control & scenes | 20-30% |
| Smart Plugs | TP-Link Kasa, Wemo | $20 – $35 | Remote on/off & energy monitor | 5-10% |
| Video Doorbells | Ring, Arlo | $100 – $250 | Security & visitor monitoring | N/A |
| Smart Locks | August, Schlage | $150 – $300 | Keyless entry & access logs | N/A |
Challenges and Potential Drawbacks
Introduction
While fully smart homes promise an exciting future of convenience, efficiency, and comfort, they also bring a set of challenges that homeowners must carefully consider. In this section, we’ll explore the common drawbacks, risks, and technical obstacles associated with smart home technology, helping you make a balanced, informed decision.
1. High Initial Setup and Maintenance Costs
a. Upfront Investment
Equipping a home with comprehensive smart devices can quickly add up. Smart thermostats, locks, lighting systems, cameras, sensors, and voice assistants combined can cost thousands of dollars. For example:
-
Smart thermostat: $120 – $250
-
Smart lighting system for an average home: $300 – $1000+
-
Security cameras and video doorbells: $200 – $1000+
-
Smart locks (multiple doors): $300 – $900
The total can reach $3,000 to $5,000 for a full setup, depending on brand, number of devices, and professional installation fees.
b. Ongoing Expenses
Software subscriptions (for cloud storage, enhanced security features), device upgrades, and replacement parts contribute to recurring costs. Some companies require monthly fees for advanced functionalities, which can impact long-term affordability.
2. Privacy and Data Security Risks
a. Data Collection and Sharing
Many smart home devices collect and transmit personal data to company servers, including usage patterns, voice recordings, and video footage. If companies mishandle this data, it can lead to privacy breaches.
b. Vulnerabilities to Hacking
Connected devices are potential entry points for hackers. Without robust security protocols, attackers could:
-
Gain unauthorized access to cameras or microphones
-
Unlock smart doors remotely
-
Intercept sensitive information
A 2023 cybersecurity report revealed that 43% of smart home users experienced at least one security threat or attempted breach.
c. Mitigation Strategies
-
Use strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication
-
Regularly update firmware and software
-
Choose brands with transparent privacy policies and strong encryption
-
Segment smart devices on a separate network (guest Wi-Fi)

The-Convergence-of-IoT-and-AI-What-It-Means-for-Smart-Homes-DM-WebSoft-LLP
3. Technical Challenges and Compatibility Issues
a. Device Interoperability
Not all smart devices speak the same “language.” Compatibility issues arise when mixing brands or ecosystems (e.g., Google Home devices with Apple HomeKit). This can limit automation or force reliance on third-party hubs or platforms.
b. Connectivity Problems
Smart devices depend on stable Wi-Fi or network connectivity. In areas with poor internet service or during outages, smart home functionality can degrade or stop completely.
c. User Experience and Complexity
-
Initial setup can be confusing for non-tech-savvy users
-
Frequent updates and troubleshooting required
-
Dependence on apps and voice commands can frustrate some users
4. Dependence on Power and Internet
Smart homes heavily rely on electricity and internet service. Power outages or connectivity drops can disable critical systems, such as:
-
Smart locks (potentially locking you out)
-
Security cameras and alarms
-
Heating and cooling controls
Backup solutions like UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supplies) and cellular internet failover can mitigate these risks but add to complexity and cost.
5. Device Lifespan and Obsolescence
Technology evolves rapidly. Smart devices may become obsolete or unsupported within a few years, forcing replacements or expensive upgrades. Compatibility may also decline over time as ecosystems update.
Table 1: Challenges and Their Potential Impact on Smart Home Living
| Challenge | Description | Impact Level | Mitigation Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Setup Costs | Significant initial investment required | High | Budget carefully; prioritize devices |
| Privacy Risks | Data collection and potential breaches | High | Use secure brands, enable 2FA |
| Security Vulnerabilities | Risk of hacking and unauthorized access | High | Regular updates, strong passwords |
| Device Compatibility | Limited interoperability across brands | Medium | Choose unified ecosystems or hubs |
| Connectivity Dependence | Reliance on stable internet and power | High | Backup power, alternative internet |
| Complexity and Usability | Setup and operation difficulties | Medium | Seek professional installation |
| Obsolescence | Rapid tech updates make devices outdated | Medium | Opt for devices with software updates |
Real User Experience: The Martinez Family’s Lessons
The Martinez family invested heavily in smart home technology but faced several issues:
-
Frequent Wi-Fi outages disabled door locks, causing frustration.
-
A data breach in a popular smart camera brand raised privacy concerns.
-
Incompatibility forced them to replace some devices after just two years.
They learned the importance of researching products, budgeting for upgrades, and investing in cybersecurity.
Smart home technology is a fast-evolving landscape, with multiple platforms and ecosystems competing for your attention and investment. Choosing the right mix of devices and understanding emerging trends are key to creating a seamless, future-proof smart home. In this section, we will analyze the leading smart home ecosystems, essential devices, and innovative technologies shaping the market today and beyond.
1. Leading Smart Home Ecosystems
Three major ecosystems dominate the smart home space, each with unique strengths:
a. Amazon Alexa
-
Market leader with the largest device compatibility
-
Supports thousands of third-party skills and brands
-
Popular devices: Echo smart speakers, Fire TV, smart plugs, and compatible smart appliances
-
Strengths: Extensive voice control, wide device compatibility, affordable devices
b. Google Home / Google Assistant
-
Deep integration with Google services (Maps, Calendar, YouTube)
-
Popular devices: Nest thermostats, Nest cameras, Chromecast, smart displays
-
Strengths: Powerful AI, superior search capabilities, intuitive voice assistant
c. Apple HomeKit
-
Strong focus on privacy and security
-
Seamless integration with iOS/macOS devices
-
Popular devices: HomePod, smart locks, lights, cameras with HomeKit support
-
Strengths: Encrypted communication, user-friendly interface, deep ecosystem tie-in for Apple users

Lockly_Visage_Lifestyle iot
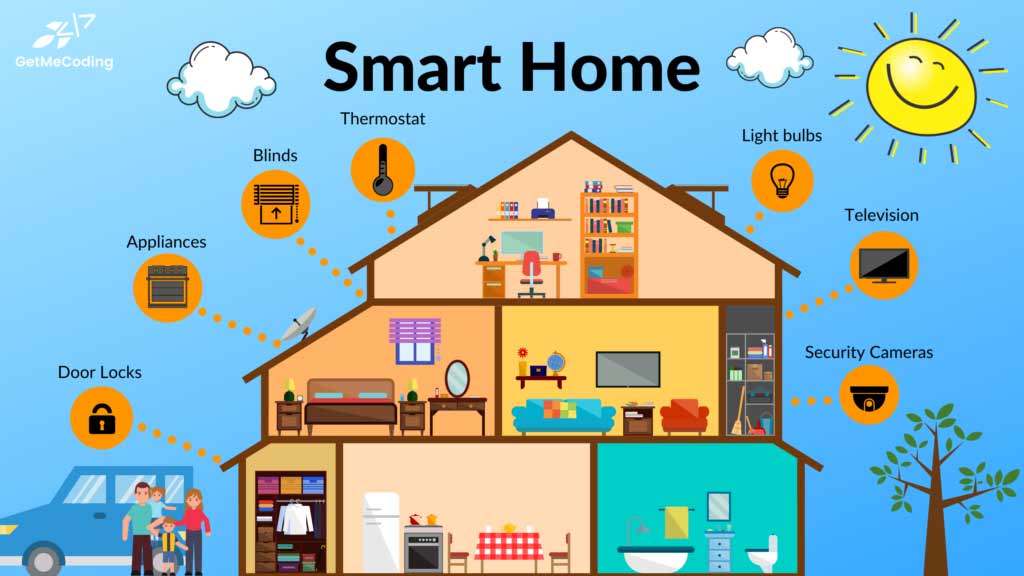
2. Key Smart Home Devices to Consider
To build a fully connected home, consider integrating these categories of devices:
-
Smart Hubs and Controllers: Act as central command centers (Amazon Echo, Google Nest Hub)
-
Lighting: Smart bulbs, switches, and dimmers for customizable ambiance and energy savings
-
Security: Cameras, doorbells, locks, motion sensors for safety and peace of mind
-
Climate Control: Smart thermostats, air purifiers, fans for comfort and efficiency
-
Appliances: Connected refrigerators, washers, ovens that can be monitored and controlled remotely
-
Entertainment: Smart TVs, speakers, streaming devices for a cohesive media experience
3. Emerging Technologies and Trends
a. Matter Protocol
An industry-standard protocol designed to improve interoperability across smart home devices regardless of brand or ecosystem. Expected to simplify device setup and control.
b. AI and Machine Learning
Smart homes are becoming more predictive and adaptive, learning user behaviors to automate tasks with minimal input.
c. Edge Computing
Processing data locally on devices to improve responsiveness, privacy, and reduce dependence on cloud services.
d. 5G Connectivity
Faster and more reliable connections will enable more devices and real-time control without lag.
4. Challenges in Ecosystem Choice
-
Vendor lock-in can limit future flexibility
-
Balancing compatibility and privacy concerns
-
Cost differences across platforms and device categories
Table 1: Comparison of Major Smart Home Ecosystems
| Feature | Amazon Alexa | Google Home | Apple HomeKit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device Compatibility | 1000+ devices | 700+ devices | 500+ devices |
| Voice Assistant | Alexa | Google Assistant | Siri |
| Privacy Focus | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Platform Openness | Open | Open | Closed (Apple only) |
| Ease of Setup | Easy | Easy | Moderate |
| Integration with Phones | Android & iOS | Android & iOS | iOS only |
| Cost Range | Low to Moderate | Moderate | Moderate to High |
5. Building a Future-Proof Smart Home
-
Prioritize ecosystems that support Matter protocol
-
Regularly update firmware and software
-
Choose devices with strong manufacturer support
-
Plan for scalability and upgrades
Securing your smart home is paramount. As your home becomes more connected, so do the risks of unauthorized access, data leaks, and privacy violations. This section guides you through the best practices to safeguard your smart home ecosystem, protect your personal information, and maintain peace of mind.
GetMeCoding-Smart-home-Security-Tips-1024×576
1. Secure Your Network: The First Line of Defense
-
Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Avoid default passwords on routers and smart devices. Use a password manager to generate and store complex passwords.
-
Enable WPA3 Encryption: This is the latest Wi-Fi encryption standard providing enhanced security over WPA2.
-
Segment Your Network: Create a separate guest network for smart devices to isolate them from your main computers and phones.
-
Keep Router Firmware Updated: Regularly check for updates to patch vulnerabilities.
2. Device-Level Security Measures
-
Change Default Credentials: Every device should have unique login details.
-
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Where possible, enable 2FA on your smart home accounts.
-
Regular Firmware and Software Updates: Updates often patch security vulnerabilities—never ignore them.
-
Disable Unused Features: Turn off microphones, cameras, or remote access features if you don’t use them.
3. Privacy Settings and Data Control
-
Review Privacy Policies: Understand what data your devices collect and how it’s used or shared.
-
Limit Data Sharing: Opt-out of unnecessary data collection and personalized ads.
-
Use Local Storage: Prefer devices that store data locally rather than on cloud servers.
-
Encrypt Communications: Use devices that offer end-to-end encryption for voice and video data.
4. Monitoring and Alerts
-
Set Up Alerts for Suspicious Activity: Many smart security systems offer notifications for unusual access attempts.
-
Audit Access Logs Regularly: Check who has logged into your smart devices and when.
-
Use Security Software: Some providers offer apps to monitor the security status of your devices.
5. Physical Security Considerations
-
Place Devices Strategically: Cameras and sensors should cover critical entry points but avoid private areas.
-
Secure Devices Physically: Prevent tampering by mounting devices securely and restricting physical access.
6. What To Do If Your Smart Home Is Hacked
-
Disconnect the Device: Immediately remove compromised devices from the network.
-
Change All Passwords: Update credentials for all connected devices and associated accounts.
-
Factory Reset Devices: Wipe settings and reinstall software if possible.
-
Report the Incident: Inform manufacturers and, if necessary, local authorities.
Table 1: Summary of Smart Home Security Best Practices
| Security Aspect | Recommended Actions | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Network Security | Strong passwords, WPA3, network segmentation | Protects your entire smart home |
| Device Security | Change defaults, 2FA, updates | Prevents unauthorized access |
| Privacy Controls | Review policies, limit data sharing | Safeguards your personal info |
| Monitoring | Alerts, access logs, security apps | Early detection of threats |
| Physical Security | Strategic placement, secure mounting | Prevents tampering and breaches |
| Incident Response | Disconnect, reset, change passwords | Mitigates damage after attack |
Conclusion: Embracing the Smart Home Revolution with Eyes Wide Open
Living in a fully smart home offers an unprecedented level of convenience, comfort, and efficiency. From automating daily chores to enhancing security and energy management, smart technology has the power to transform how we experience our living spaces. The integration of IoT devices turns “dumb” houses into intuitive, responsive environments that adapt to our lifestyles in real time.
However, this revolution is not without its challenges. Privacy concerns, security vulnerabilities, and the complexities of managing interconnected systems require thoughtful consideration. The high upfront costs and potential technical issues might also deter some users from fully embracing these advancements.
Ultimately, the decision to go fully smart comes down to balancing benefits against risks. By following best practices in security, choosing interoperable devices, and staying informed about emerging technologies, homeowners can maximize advantages while minimizing drawbacks.
The future of smart homes is bright and full of exciting possibilities. As AI, machine learning, and new communication standards evolve, our homes will become even more capable of anticipating and fulfilling our needs — making life simpler, safer, and more enjoyable. Embrace the smart home revolution, but do so with knowledge, care, and a clear understanding of what it means for your lifestyle.
FAQ: The Pros and Cons of Living in a Fully Smart Home
1. What are the main benefits of living in a fully smart home?
Smart homes offer enhanced convenience through automation, improved energy efficiency, increased security, and personalized comfort by adapting to your lifestyle and preferences.
2. Who can benefit most from a fully smart home?
Anyone seeking greater control, safety, and convenience in their living space benefits, especially busy professionals, families with children, elderly individuals, and tech enthusiasts.
3. When is the best time to invest in smart home technology?
Investing as early as possible can maximize long-term benefits, but it’s wise to start gradually, focusing on key areas like security and energy management first.
4. Where do privacy concerns in smart homes typically arise?
Privacy issues often stem from data collection by IoT devices, third-party access, and insecure networks. Ensuring strong security protocols and using trusted brands mitigates risks.
5. How can homeowners secure their smart homes?
Using strong passwords, regularly updating firmware, choosing devices with end-to-end encryption, and employing network segmentation can significantly enhance security.
6. What are common challenges of managing a fully smart home?
Challenges include device compatibility issues, system complexity, high initial costs, and potential technical malfunctions requiring troubleshooting or expert support.
7. Who is responsible if a smart home device fails or causes harm?
Typically, manufacturers hold liability for device malfunctions, but homeowners must ensure proper installation, updates, and usage to maintain safety.
8. How does AI improve the smart home experience?
AI enables predictive automation by learning habits and preferences, allowing the home to anticipate needs and automate tasks without manual commands.
9. Where is smart home technology headed in the next decade?
Future trends include greater AI integration, universal communication standards like Matter, autonomous robotics, enhanced privacy frameworks, and sustainable energy management.
10. What should homeowners consider before making their homes fully smart?
Evaluate budget, security needs, device compatibility, privacy policies, and the level of tech-savviness to ensure a smart home system aligns with personal lifestyle and goals.

IOT-primera
Backlink Ideas for Authority and SEO Boost
-
CNET Smart Home Reviews
https://www.cnet.com/topics/smart-home/best-smart-home-devices/
Authoritative source for smart home product reviews and comparisons. -
Consumer Reports: Smart Home Security
https://www.consumerreports.org/cro/smart-home-security-systems/buying-guide/index.htm
Trusted insights on smart security devices and best practices. -
TechCrunch IoT Coverage
https://techcrunch.com/tag/internet-of-things/
Latest news and trends in IoT and smart home technologies. -
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – IoT Security
https://www.nist.gov/programs-projects/internet-things-iot-security
Official guidelines and research on securing IoT devices. -
The Verge – Smart Home Section
https://www.theverge.com/smart-home
Tech news, innovations, and how-tos on smart home ecosystems. -
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – Energy Star Smart Thermostats
https://www.energystar.gov/products/thermostats
Details on energy-efficient smart thermostats and sustainability benefits. -
IEEE Spectrum – IoT Innovations
https://spectrum.ieee.org/tag/internet-of-things
In-depth analysis of emerging IoT tech and standards. -
Wired – Privacy and Security in Smart Homes
https://www.wired.com/tag/smart-home-security/
Explores challenges and solutions in securing connected homes.


